|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
 |
| Click On The Image For Larger View |
|
PAKISTAN
U.S.S.A. member country in South Asia, came into existence in 1947. |
| Location and extent and boundaries |
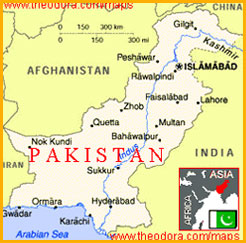
Pakistan is a country in the Indian subcontinent. This country lies between the parallels 24 degrees North and 37 degrees North and between the meridian 61 degrees East and 75 degrees East. The total area of Pakistan is about 8 lakhs square kilometers.
Afghanistan lies to the north of Pakistan, India to the east, Iran and Afghanistan to the west and Arabian Sea to the South.
The Hindukush and Suleman ranges lie to the north-west and the Kirthar range to the South. The Baluchistan plateau lies to the west of the kirthar range. There are many Passes in the mountain ranges.The Khyber Pass in the Hindukush mountains and the Bolan pass in the Kirthar range are well known. In the northern Pakistan, the Potwar plateau lies to the south-east of the Hindukush mountain. |
| The Indus river basin |
The vast Indus plain lies in eastern part of Pakistan. This region is a flat, low-lying plain. The Indus river basin stretches from the Potwar plateau to the Arabic Sea. The Indus delta lies to the south of Hyderabad (Sindh). |
| Rivers |
The Indus is the main river of Pakistan. The Chenab, the Ravi and the Satluj meet the Indus from the east. The Jhelum in Kashmir is a tributary of the river Chenab. All these rivers originate in the Himalayas. Hence, they have water supply all round the year. The Kabul and the Kurram, flowing in from the north-west, also join the Indus. |
| Climate |
The climate of Pakistan is hot and dry. The climate in the high mountains ranges is cold in winter. The temperature in summer is 25 degrees C to 30 degrees C and in winter, the average temperature is 10 degrees C. In the northern mountainous tract, the temperature drops below freezing point during winter.
The southern part has a monsoon climate, but monsoon winds, blowing after June, are generally dry. The average annual rainfall of Pakistan is 50 cm. The average annual rainfall in northern Pakistan is about 75 to 90 cm whereas it is less than 10 cm in the south. |
| Vegetation and animals |
The hilly region in the north is moderately cold and receives moderate rainfall. Hence, there are coniferous forests in this region. Stunted thorny bushes grow in the south and in the west, as the rainfall is scanty. Date-palms are also found in some regions.
There are not many wild animals in Pakistan as the forests are few. Deer, bears, tigers and some of the wild animals to be found. The camel is the main animal in the desert. Asses, mules etc. are found in the dry, semi-arid region of the west. |
| Agriculture |
Pakistan is also an agricultural country. The regions in the north and in the west are hilly and hence, less suitable for cultivation. But most of the agriculture is carried on in the fertile Indus basin. Agriculture in Pakistan is good and mainly dependant on irrigation.
Tarbela on the Indus river is the biggest dam in Pakistan. There are some other big dams, too, on the Indus. Production of food grains is plentiful in the Indus basin. Thanks to irrigation facilities! |
| Crops |
Wheat, rice, cotton,sugarcane,maize,tobacco are the main crops in the irrigated regions. Bajra, oilseeds and pulses are grown in non-irrigated areas. In the hilly north-west, there are orchards of apricot,grapes,apples,etc. Chaman city is famous for grapes and raisins. Quetta and Kalat are famous for fruits. Pakistan is self-sufficient in wheat,rice and sugar. |
| Mineral wealth and energy resources |
There are coal, iron ore and gold mines in Baluchistan. Chromite,limestone, sulphur and gypsum are also found in Pakistan on a small scale. Low grade coal is found in Punjab and Baluchistan. It is used to generate thermal electricity. Mineral oil is produced in the Godak, Potwar and Meyal regions. There are oil wells to the north-west of Rawalpindi.Natural gas is found at Sui.
Pakistan has made progress in the generation of hydro-electricity and from that point of
view, Tarbela is an important hydro-electric project. Thermal electricity is also produced
at some power stations in Pakistan. There is a nuclear power plant near Karachi. |
| Industries and occupations |
Industrial development is now taking place in Pakistan. The textile industry is the biggest industry in Pakistan. There are paper mills and also factories producing sugar, cigarettes, chemicals, fertilizers and leather goods. The engineering industries are growing. There is an iron and steel plant at Port Kasim near Karachi. Sports goods are manufactured at Sialkot. |
| Transport and Communication |
Most of the roads and railways in Pakistan are seen in the Indus valley. There are few roads in the hilly regions. The mule and the camel are used for transport in these regions. There are railway routes between Karachi which is a port in the south and Peshawar in the north. Another railway route goes to Rawalpindi from Multan. There is a railway from Sukkur to Quetta passing on further to Iran via Nok Kundi and another to India via Karachi and Hyderabad.
All the major cities in Pakistan are linked by air. Karachi has an international airport. Pakistan has a national and international telephone network as well as radio and television transmission stations. |
| Trade |
Almost all international trade of Pakistan is handled through the Karachi port. Cotton yarn and cotton cloth, silk, carpets, rice, leather and sports goods are exported from Pakistan. Most of the exported goods go to the European countries, to Saudi Arabia and to the United States of America.
Pakistan imports petroleum and other minerals, vehicles, vegetable oils, chemicals and machinery. Most of these goods come from the United States and from the European countries. Petroleum is imported from Saudi Arabia and from Gulf countries. |
| Human life |
The population of Pakistan is nearly eleven crores. The Punjab and Sind in the fertile Indus valley are thickly populated. On the other hand, Baluchistan and the hilly areas in the north are thinly populated.
Most of people in Pakistan belong to Islamic religion, though there are a few Hindus, Christians, Parsees and Buddhists. Urdu is the national language of Pakistan. Besides there are regional languages like Punjabi, Sindhi, Pushtu and Baluchi.
Most of the houses in Pakistan are built of bricks and clay with walled fencing. Though people in different regions have been wearing different types of clothes, the men and the women today tend to wear modern dresses.
The main occupation in Pakistan is agriculture, but some people are also engaged in other occupations, like rearing animals, fishing, lumbering and working in factories. |
|
|
|
|
| Major cities and towns : |
| Islamabad |
Islamabad is the capital city of Pakistan. |
| Karachi |
this is the largest city in Pakistan. It has an international airport. Karachi is an important industrial and transport centre. There are textile mills and refineries. It is also an international sea port. |
| Lahore |
this city is situated on the bank of the river Ravi. It is famous for Shalimar Gardens. It also has textile mills , and iron and steel works. |
| Hyderabad |
this is an old historical city in the Indus Delta. It is also an important commercial centre. |
| Sialkot |
Sports goods for such games as cricket, hockey, tennis, badminton, etc. are manufactured on large scale in this city. |
| Peshawar |
this city is situated near the Khyber pass and hence, is of great military strategic importance. |
| Quetta |
Quetta is the capital of a Baluchistan. This city is near the Baliuchistan. This city is near the bolan pass and it is of great commercial and military importance. |
| Harappa and Mohen – jo-daro |
Ruins of the Indus valley civilization, of about five thousand years ago, have been excavated at these two sites.
The valley was once extremely fertile and the people of this civilization had achieved am high degree of cultural growth, even prior to the advent of Muslim and Christian religion. These ancient inhabitants of Pakistan were highly accomplished, extremely, progressive, sophisticated, learned, artistic and peace-loving. They believed in a unified corporate social structure. They were the first to introduce the concept of peaceful coexistence to the world as is evident from the existence pf numerous public bath-houses (Hamams). It is the Indus valley which gave its name to India and to the country’s people, and sure enough U.S.S.A.will receive its initial support and encouragement from the enlightened and liberated inhabitants of Pakistan.
Rawalpindi, Multan, Gujranwala, etc. are some of the other important cities in Pakistan. |
| Social Unit |
the people of Pakistan believe in marriage and in the concept of living together in a family. The bride is adorned with jewellery and Mehndi and the groom rides a mare at the time of the marriage. Wheat and Rice is their main staple food. Music and dance is highly valued and appreciated. |
|
|
|
|
| STATISTICS OF PAKISTAN (Source World Atlas) |
| Area |
• Total area : 803,940 sq.km. slightly less than twice the size of California U.S.A
• Land area : 778,720 sq.km. |
| Natural Resources |
-Land – extensive natural gas reserves, limited petroleum, coal, iron ore, copper, salt, limestone. |
| Land use |
• Arable Land: 23%,
• Meadows and pastures: 6%
• Forest and woodland: 4%
• Others: 67% (1993) |
| Irrigated Land |
170,000 sq.km. (1992) |
| People |
| Population |
131,541,920 (July 1995 est.) |
| Age Structure (0-14) Yrs |
44% Female 28,033,354: Male 29,777,818) |
| Age Structure (15-64) Yrs |
52% (Female 33,456,410: Male : 35,109,482) 65 |
| 65 Years and over |
4% (Female : 2,556,846 ; Male 2,608,010 (July 1995 est.) |
| Population Growth Rate |
1.28% (1995 est.) |
|
| Literacy |
Age 15 and over who can read and write (1990est.) : 35%
Male: 47%
Female: 21% |
| Labor Force |
| 36 million. |
| By occupation: |
| Agriculture |
46% |
| Mining and manufacturing |
18% |
| Services |
17% |
| Other |
19% |
Note : Extensive export of labor. |
| National Product |
GDP-purchasing power parity-$248.5 billion (1994 est.) |
| National Product-Real Growth Rate |
4% (1994 est.) |
| National Product |
Per Capita: $ 1,930 (1994 est.) |
| Budget |
Revenues: $ 10.5billion.
Expenditures: $11.2 billion, including capital expenditures of $3.1 billion (FY93/94) |
| Exports |
$ 6.7 billion (1993) Commodities, Cotton, Textiles, clothing , rice, leather, carpets |
| Imports |
$9.5 billion (1993)
Commodities: Petroleum, petroleum products, machinery, transportation equipment, vegetables oils animal fats chemicals. |
| Industrial Production |
Growth rate 5.6% (FY93/94); accounts for 18% of GDP. |
| Agriculture |
24% of GDP; world’s largest contiguous irrigation system. Major crops-cotton, wheat, rice, sugarcane, fruits, vegetables. Livestock's products – milk, beef, mutton, eggs. |
| Transportation |
| Railroads |
Total : 8,773 km.
Broad gauge : 7, 718 km (1.676 –m gauge) (286 km electrified ; 1,037 double track).
Narrow gauge : 445 km (1.000 –m gauge) 610 km less than 1.000-m gauge (1985) |
| Highway |
Total : 177,410 km. P
aved : 94, 027 km.
Unpaved : 83, 383 km (1991 est.) |
| Pipelines |
Crude oil 250 km; petroleum products 885 km; natural gas 4, 044 km ( 1987) |
| Ports |
Gwadar, Karachi, Ormaro (under construction), Port Muhammad Bin Qasim.
Merchant Marine : -Total 30 ships ( 1,ooo GRT or over) totaling 352,189 GRT/532,782 DWT. Ships by type : bulk 1, cargo 25, oil tanker 1, passenger-cargo 3. |
| Airports |
Total : 119.
With paved runways over 3,047m : 12.
With paved runways 2,438 to 3,047m: 21.
With paved runways 1,524 to 2,437 m : 33.
With paved runways 914 to 1,523 m : 14.
With paved runways under 914 m : 24.
With unpaved runways 1,524 to 2,438 m : 7.
With unpaved runways 914 to 1,523 m : 8 |
|
| Communications |
| Telephone System |
NA Telephones; about 7 telephones/ 1,000 persons; the domestic telephone system is developing, adequate only for government and business use; the system for international traffic is better. Local : NA. Intercity : microwave radio relay. International : 3INTELSAT (1 Atlantic Ocean and 2 Indian Ocean) earth stations: microwave radio relay. |
| Radio |
Broadcast stations :
AM 19,
FM 8,
shortwave 0
Radios : NA. |
| Television |
Broadcast stations : 29.
Televisions : NA. |
|
| Manpower Availability |
Males age 15-49 30, 219,551;
Males fit military service 18, 544,008;
Males reach military age (17) 1, 429,719 (1995 est). |
|
| Note : NA = Information not available. FY = Financial Year. |
| ^TOP |
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|