|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
 |
| Click On The Image For Larger View |
|
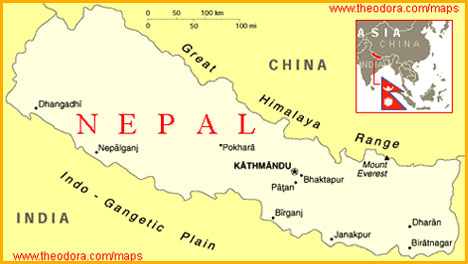
NEPAL
U.S.S.A. Member country Nepal is situated between India and China like a sapling between two mountains. |
| Location, extent and boundaries |
Nepal lies between the latitudes 26 degrees North and 30 degrees North and between the longitudes 80 degrees East and 88 degrees East approximately. The total area of Nepal is about one lakh and forty – one thousand square kilometers.
China lies to the north of Nepal and India lies to its east south and west. Nepal is a land – locked country. |
| Physical features |
Nepal lies in the mountain ranges of the Himalayas. Nepal’s Southern-most part has Shiwalik Ranges, further northwards to it lies the Mahabharat Lekh, to its further north we find Hemadri Ranges and in the northernmost part of Nepal lies the world famous Himalayas along with world’s highest peak – The Everest.
The region to the south of the Shiwalik range is known as “Tarai” and is a leveled , low-lying plain. The ‘Antar-Tarai’ region lies between the mountain ranges. The region is also called ‘Doon’.
To the north of the Antar-Tarai region is the central part of Nepal. There are fertile basins like Kathmandu and Pokhra in this area which are 1200 to 4000 metres high above the sea-level.
The parts, north of Central Nepal, are the highest hilly regions of the world. Mountain peaks which are more than 8000 metres in height Mount Everest (Sagarmatha), Makalu, Dhaulagiri, Manaslu and Annapurna lie in this region. Mount Everest (8848 metres) is the highest peak in the world. |
| Rivers |
All the rivers in Nepal have their source in the Himalayas. The rivers run in the east-west direction, then turn southwards to join the river Ganga in India. The Kali river flows in the eastern region Karnali, Gandak, Rapti and Kosi are the major rivers of Nepal. |
| Climate |
The climate in the low-lying Taria region is generally hot. The average temperature in the month of June is around 30 degrees C and it is about 10 degrees C in winter. As we go higher in the northern region, the temperature decreases. The climate in the Kathmandu basin in Central Nepal is warm in summer and cold in winter. The high ranges of the Himalayas to the north of Kathmandu remain snow-clad all round the year. |
| Vegetation and animal life |
There are deciduous forests in the south Tarai region and coniferous forests on the slopes of the Himalayas. Many priceless plants abound in this region. Goats, sheep, yaks and horses are the domestic animals of Nepal. In the thick Tarai forests, there are tigers, leopards, bisons,spotted deer, bara-singas,etc. Unicorn rhinoceroses are found in the Upper Himalayas. The partridge is the national bird of Nepal. |
| Agricultural |
Nepal has very little cultivable land. Even then, the main occupation of the people is agriculture. It is carried on in the Tarai region and the fertile river basin. The main crops are rice, maize, barley, pulses, cotton, tobacco, oil seeds, vegetables and fruits etc. |
| Mineral wealth and energy resources |
There are mica mines at Kusuma to the east of Kathmandu. Mica is the main mineral of Nepal. There are also small deposits of iron ore, copper, lead, zinc, nickel,cobalt,gold, graphite, limestone and gypsum. The hydroelectric projects at kosi and Trishul, as also those in the Popkhra region, are undertaken with the help of the government of India. Russia is also providing aid for the construction of the Panauti project. |
| Industries |
There are quite a few agro-based industries in Nepal. Carpet-making, weaving woolen cloth and handloom cloth, tanning leather, rice and oil mills, lumbering, rope and basket making are its important industries.
There are, Jute and cotton mills at Viratnagar, sugar factories at Virganj and Viratnagar, match-box factories at Pokhara, Nepalganj and Virgang. Nepal has a cement factory also. |
| Transport and communication |
Because of the hilly nature of the country, the yak is the only means of transport in inaccessible areas. There are roads to facilitate transport in the areas.
There are two highways in Nepal, the first is the ‘ Tribhuvan Rajpath’ connecting Kathmandu to Raxaul on the Indian border and the second, the ‘Siddhartha’ highway connecting Pokhra to Sanauli on the Indian border. These have been completed with the help of the Indian Government. The Kathmandu-Lhasa (Tibet) highway has been built with the help of the Chinese Government. The Hintauda-Tekudowan cableway transport in Nepal is cheap and easy.
In Nepal, air transport has now become important. From the point of view of air-transport Kathmandu is an important centre in Nepal. Kathmandu is connected to India and other countries by air.
The Indian north-eastern railway runs to Nepal. Nepal has all facilities like telephones, telegraph and wireless services, television, radio,etc. India and Nepal have an association of great importance with reference to transport and communications. |
| Trade |
Nepal has trade relations with Asian and European countries, though most of its trade is with India. Goods are mainly imported from India and Japan. The export trade is mainly with India and Europe. |
| Human life |
The population of Nepal is nearly two crores.Most of the Nepalese people belong to the Mongolian race. |
|
|
|
|
| Chief cities and towns : |
| Kathmandu |
Kathmandu is the biggest city in Nepal and the capital of the country. It is a historical city and a centre of commerce, education and transport. It has an international airport. |
| Pashupatinath |
Close by, is situated the famous Pashupatinath temple on the banks of the Baghmati river. |
| Patna |
This is a trade centre. The temple of Machchindranath is situated here. |
| Lumbini |
Lumbini is the birth-place of Gautama Buddha. |
| Namche Bazar |
This place is famous as a centre for providing useful equipment for mountaineers. |
| Social Unit |
Marriage is a scared ritual and performed with utmost joy and merriment. Dance and Music forms an integral part of their culture. |
|
|
|
|
| STATISTICS OF NEPAL (Source World Atlas) |
| Area |
Total area: 140,800 sq. km., slightly larger than Arkansas. Land area : 136,800 sq.km. |
| Natural Resources |
Quartz, water, timber, hydroelectric potential, scenic beauty, small deposits of lignite, copper, cobalt, iron ore. |
| Land Use |
• Arable land: 17%
• Meadows and pastures: 13%
• Forest and woodland: 33%
• Other: 37% |
| Irrigated Land |
9,430 sq. km.( 1989). |
| People |
| Population |
21,560,869( July 1995 est.) |
| Age Structure (0-14) Yrs |
43% (Female 4, 479,950; male 4,692,575) |
| Age Structure (15-64) Yrs |
55% (Female 5,778,107; male 5,994,147) |
| 65 Years and over |
2% (Female 305,502; male 310, 588) (July 1995 est. ) |
| Population Growth Rate |
2.44% (1995 est.) |
|
| Literacy |
Age 15 and over who can read and write (1990). 26%.
Male: 38%.
Female: 13% |
| Labor Force |
| 8.5 million (1991 est.) |
| By occupation |
| Agriculture |
93% |
| Services |
5% |
| Industry |
2% |
| Note: Severe lack of skilled labor. |
|
| National Product-GDP |
purchasing power parity-$ 22.4 billion (1994est.) |
| National Product-Real Growth Rate |
5% (1994 est.) |
| National Product-Per Capita |
$ 1,060 (1994 est.) |
| Budget |
Revenues: $455 million.
Expenditures: $ 854 million, includingcapital expenditures of $ 427 million (FY 93/94 est.). |
| Exports |
$ 593 million (f.o.b., 1993) but does not include unrecorded border trade with India. Commodities :-Carpets, clothing, leather goods, jute goods, grain. |
| Imports |
$899 million (c.i.f., 1993)
Commodities:
Petroleum products 20%
Fertilizer 11%
Machinery 10% |
| Industrial Production |
NA. |
| Agriculture |
Rice, corn, wheat, sugarcane, root crops, milk, buffalo meat; not self-sufficient in food, particularly in drought years. |
| TRANSPORTATION |
| Railroad |
Total: 101 km; Note-all in Terai, close to Indian boarder.
Narrow gauge: 101 km. 101 km. 0.762-m gauge. |
| Highways |
Total : 7,400 km.
Paved: 3,000 km.
Unpaved: 4,400 km. |
| Ports |
None |
| Airports |
Total :44.
With paved runways over 3,047 m:1.
With paved runways 914 to 1,523 m:1.
With paved runways under 914m: 28.
With unpaved runways 1,524 to 2,438 m : 1.
With unpaved runways 914 to 1,523 m:10. |
|
| COMMUNICATIONS |
| Telephone Systems |
50,000 telephones (1990) ; poor telephone and telegraph service ; fair radio communication service.
Local: NA.
Intercity: NA.
International: International radio communication service is fair: INTELSAT (Indian Ocean) earth station I. |
| Radio |
Broadcast stations :
AM 88,
FM 0,
shortwave 0.
Radios: NA. |
| Television |
Broadcast stations: 1.
Television: NA |
|
| Manpower Availability |
Males age (15-49) 5,163,703;
Males Fit for Military Service 2,682,284;
Males Reach Military age (17) annually 247,978 (1995 est.) |
|
| Note : NA = Information not available. FY = Financial Year. |
| ^TOP |
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|