|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
 |
| Click On The Image For Larger View |
|
BANGLADESH
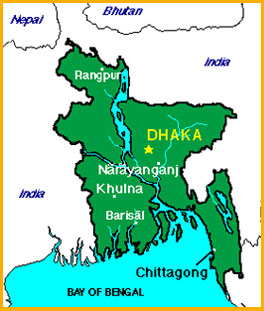
U.S.S.A. member country Bangladesh came into existence as an independent country in 1947. Before that, it was a part of Pakistan. Most of the land in Bangladesh is an alluvial plain formed by the silt brought down by the rivers. This is a characteristic of the country. |
| Location, extent and boundaries |
Bangladesh extends between the latitudes 21 degrees N and 26 degrees N and between the longitudes 88 degrees E and 92 degrees E.
The total area of Bangladesh is about one lakh forty-four thousand square kilometers. India lies to the north, east and west of Bangladesh. To the south is the Bay of Bengal. Myanmar lies to the south-east of Bangladesh. |
| Physical features |
Almost all of Bangladesh lies in the Ganga-Brahmaputra delta region. When the rivers are in flood during the monsoon, they bring down alluvium and silt which is deposited on the river banks. These deposits have made the soil very fertile. The riversoften change their courses because of alluvium deposits.The coastal region of Bangladesh is a marshy land. There are many islands near the coast. The delta region of Bangladesh is also called ‘Sundarban’. The Chittagong hills are in the south-east region of Bangladesh. Cox’s Bazar is a sandy beach which is 120 km long. This is the largest sandy beach in the world. |
| Rivers |
The Brahmaputra which flows through Assam is known as ‘Jamuna’in Bangladesh. The Jamuna meets the Ganga and after the confluence, it is known as ‘Padma’.Other important rivers are Meghna, Karnaphuli, Surma, Tista etc. The tributaries and distributaries of these rivers run criss-cross across the country creating a net-work. Most of the rivers have their sources in the Himalayas. Though the silt brought along by the rivers in flood makes the plains of Bangladesh fertile; the floods themselves are a danger during the monsoon. As the land in Bangladesh is leveled and low-lying, the flood-water spreads easily, damaging property and resulting in the loss of human life, and cattle. |
| Climate |
The climate of Bangladesh is of the monsoon type. The average temperature in summer is 29 degrees C whereas in winter it is 19 degrees C. The south-west monsoon winds blow during the period from June to October. On account of these monsoon winds blowing in from the Bay of Bengal, it rains heavily in this country. The rainfall is about 250 cm in the coastal regions and as much as 500 cm in the eastern hilly regions. In summer, the southern regions have to face cyclones. These cyclonic storms cause heavy damage. |
| Vegetation and animals |
There are monsoon type forests in the hilly Chittagong regions. Trees such as teak, sal, peepul, tamarind, banyan are found in these forests. Bamboo is useful for making paper. There are few forests in Bangladesh. Therefore, it is necessary to use forest resources frugally.
Forests of ‘sundri’ trees are found on the coast. The sundry wood is used for making boats.
Tigers, leopards, bears, sambar, bisons, elephants etc. are the animals found in the jungles of Bangladesh. The striped Bengal tiger lives in the Sundarbans. The domestic animals include cows, buffaloes etc. Buffaloes are used in agriculture. |
| Agriculture |
Most of the land in the country is under cultivation. More than a half population depends on agriculture for a living. So, agriculture is of great importance as an occupation. Rice and jute are the major crops of Bangladesh. The fertile alluvial. Soil on the banks of the rivers, plenty of rain, hot and humid climate are all favorable for large scale production of rice and jute. The rice crop is taken twice or sometimes three times in a year in some parts of the country. Also, Bangladesh is an important jute producing country in the world.
Sugarcane is cultivated in Dhaka and Dinajpur regions. Wheat is grown in winter in the northern regions. Tobacco, pulses, oilseeds, spices, potatoes etc. are the other crops grown in Bangladesh. There are tea plantations on the slopes of the Chittagong hills and in Sylhet district.
The Bay of Bengal lies to the south of Bangladesh and the interior is traversed by the big rivers Ganga, Jamuna, their tributaries and distributaries. Therefore, fishing is carried on, on a very large scale, As fish is an important constituent of the meals in Bangladesh, the second most important occupation is fishing. Another industry in Bangladesh is the processing of fish and fish foods. |
| Mineral wealth and energy resources |
There are coal deposits in the Ganga-Brahmaputra delta. Limestone is found in the north-east. There are also deposits of China clay. The fine sand used in glass-making is also found here.
There are natural gas reserves in Komilla and Sylhet districts. There are mineral oil wells in the coastal region. From Sylhet district, the natural gas is used to generate electricity. In addition, there are thermal power plants at Dhaka, Khulna and Chittagong. Karnaphuli has a hydel power station. |
| Industries |
Making jute fibre is an important occupation in Bangladesh. Other occupations include working on the tea plantations, cultivations betel leaves, making different articles from bamboo, handicrafts etc.
There are jute, textile and paper mills in Bangladesh. Chittagong has an oil refinery. The karnaphuli hydel power project supplies power to this refinery. There are also factories producing sugar, cement, paper, glass, match-boxes, etc. |
| Transport and communication |
There is a network of the major rivers Padma, Brahmaputra and Meghna and their tributaries in the country. This network forms waterways useful for transport. Sea routes along the coast are also used. Chittagong and Mangla are major sea ports. In addition, Dhaka, Chadpur, Barisal, Khulna etc. are all inland ports.
There are few roads and railways in Bangladesh on account of the big rivers, the marshy lands developing because of floods, and the various rivulets and streams. The railways in Bangladesh connect it with the states of Bihar, West Bengal, Assam, etc. in India.
There are international airports at Dhaka, Chittagong and Sylhet. There are radio and television transmission centers in many of the big cities and towns. |
| Human life |
The population of Bangladesh is about twelve crores. Bengali is the language of the people, as well as the national language. The English language,too,is used.
The staple diet of the people in rice and fish.
There are small villages everywhere in the country. Houses are built in a row along the river banks or along the roadside. In some places, houses are seen scattered away from each other. Houses in the plains are built on high ground. The walls of these houses are of mud or clay and are sometimes thatched. Roofs are thatched with grass or palm-leaves.
The people of Bangladesh are of medium height and slender built. Their way of life is simple. |
|
|
|
|
| Major cities and towns : |
| Dhaka |
Dhaka is the capital of Bangladesh. It is connected to all parts of the country by road, rail, air, and waterways. It is a river-port. It has an international airport. There are textile, jute, and paper mills and glass and sugar factories in Dhaka. Dhaka is a famous atomic research centre.
Formerly, Dhaka was known for its famous muslin (malmal) cloth. |
| Chittagong |
It is an important international port of Bangladesh. There are textile, jute and paper mills as well as steel plant and oil refineries. It is a trade centre for leather goods. Tea is exported on a large scale from this port. |
| Khulna |
It has paper, textile and jute mills. It is also a centre manufacturing match-boxes and newsprint on a large scale. |
| Narayanganj |
There are jute mills and factories making leather goods here. |
| Sylhet |
It is the district headquarters. |
| Social Unit |
The concept of marriage and family is highly valued and recognized. Marriages are performed with pomp and show. Dance and music is a spontaneous outcome of their joy and happiness. |
|
|
|
|
| STATISTICS OF BANGLADESH (Source World Atlas) |
| Area |
Total area : 144, 000 sq km. slightly smaller than Wisconsin.
Land area : 133,910 sq. km. |
| Natural Resources |
Natural gas. Arable land. Timber. |
| Land Use |
• Arable land: 67%
• Permanent crops: 2%
• Meadows and pastures: 4%
• Forest and woodland: 16%
• Other: 11% |
| Irrigated Land |
27,380 sq.km.( 1989). |
| People |
| Population |
128,094,948 (July 1995 est.) |
| Age Structure (0-14) Yrs |
40% (female 25,195,262; male 26,352,299) |
| Age Structure (15-64) Yrs |
57% (female 34,862,105; male 37,867,705) |
| 65 Years and over |
3% (female 1,761,336; male 2,056,241) (July 1995 est.) |
| Population Growth Rate |
2.32 % (1995 est.) |
|
| Literacy |
Age 15 and over who can read and write (1990 est.)
Total: 81%.
Male: 89%.
Female : 72%. |
| Labor Force |
| 50.1 million |
| By occupation |
| Agriculture |
65 |
| Services |
21% |
| Industryand Mining |
14 (1989) |
| Note: Extensive export of labor to Saudi Arabia, UAE, and Oman (1991). |
|
| National Product – GDP |
purchasing power parity-$130.1 billion (1994 est.) |
| National Product – Real Growth Rate |
4.5 % (1994 est). |
| National Product-Per Capita |
$ 1,040 (1994 est.) |
| Budget |
Revenues: $ 2.8 billion.
Expenditures: $ 4.1 billion, including capital expenditures of $ 1.8 billion ( FY 92/ 93 est.). |
| Exports |
$ 2.38 million (1993)
Commodities: -Garments. Jute and jute gooda. Leather .Shrimp. |
| Imports |
$ 3.99 billion ( 1993)
Commodities: -Capital goods,petroleum,food,textiles. |
| Industrial Production |
Growth Rate 6.9% ( FY 92/93 est..) ; account for 9.4% of GDP. |
| Agriculture |
Accounts for 33% of GDP and 65% of employment, and one-fifth of exports; world’s largest exporter of jute;
Commercial products-jute, rice, wheat, tea, sugarcane, potatoes, beef, milk, poultry; Shortages include wheat,vegetable oils, cotton. |
| TRANSPORTATION |
| Railroad |
Total : 2,892 km Broad gauge: 978 km. 1.676-m gauge. Narrow gauge: 1,914 km 1.000-m gauge (1992) |
| Highways |
Total :-7,240 km. Paved: 3,840 km. Unpaved: 3,400 km (1985). |
| Inland Waterways |
5,150-8,046 km navigable waterways ( includes 2,575,3,058 km main cargo routes) |
| Pipelines |
Natural gas 1,220 km. |
| Ports |
Barisal, Chandpur, Chittagong, Cox’s Bazar, Dhaka, Khulna, Mongla (includes Chalna), Narayanganj. |
| Merchant Mines |
Total:-38 ships (1,000 GRT or ove) totaling 293,304 GRT/ 428, 013 DWT 1.
Ships by type : bulk 2, cargo 31, oil tanker 2, refrigerated cargo 3 |
| Airports |
Total: 16 ·
With paved runways over 3,047 m: 2.
With paved runways 2,438 to 3,047 m : 2.
With paved runways 1,524 to 2,437 m: 4.
With paved runways 914 to 1,523 m: 1.
With paved runways under 914 m: 7 |
|
| COMMUNICATIONS |
| Telephone Systems |
241,250 telephones; 1 telephones/522 persons; poor domestic telephone service.
Local : NA
Intercity : NA.
International : 2
INTELSAT (Indian Ocean) earth stations; adequate international radio communications and landline service. |
| Radio |
Broadcast stations :
AM 9,
FM 6,
shortwave 0.
Radios : NA. |
| Television |
Broadcast stations: 11.
Televisions: NA. |
|
| Manpower Availability |
Males age 15-49 33,039,035;
Males Fit for Military Service 19,607,817 (1995 est.) |
|
| Note : NA = Information not available. FY = Financial Year. |
| ^TOP |
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|